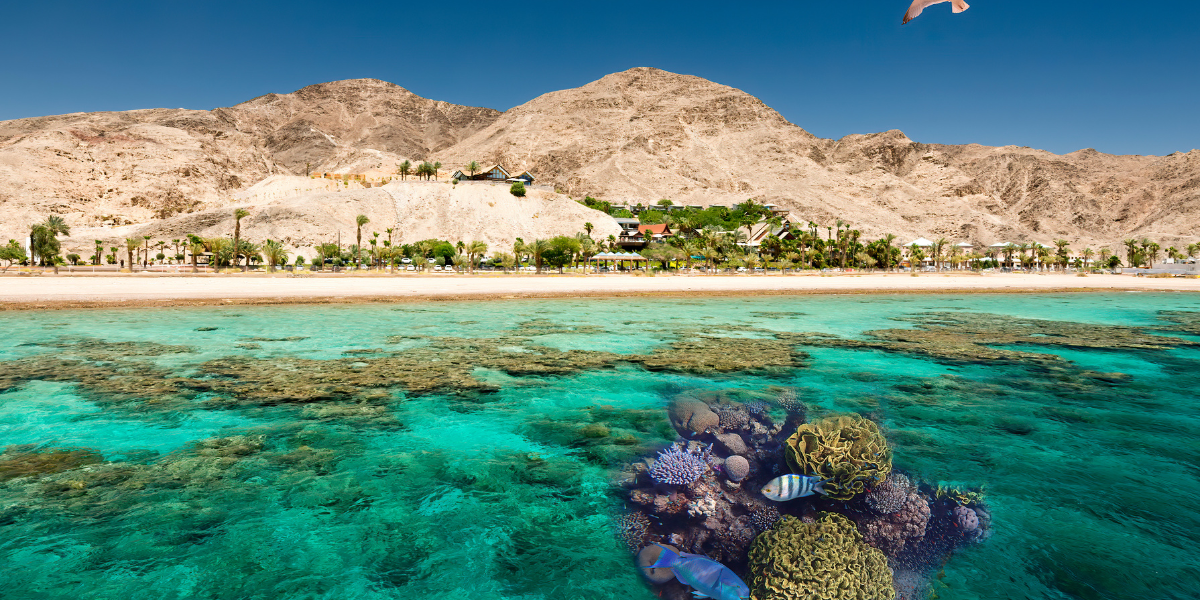
Do you know that the ocean is home to millions of species? From tiny plankton to enormous whales, marine life plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our planet’s ecosystem.
Unfortunately, human activities have caused significant damage to the marine environment, leading to a decline in biodiversity. In recent years, several factors have influenced marine biodiversity, including climate change, pollution, overfishing, habitat destruction and invasive species.
For instance, let us consider coral reefs – one of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet. These beautiful structures are home to thousands of fish species and provide essential services like coastal protection and tourism revenue. However, rising sea temperatures due to climate change are causing massive bleaching events that are killing off entire coral colonies.
This not only affects these delicate organisms but also impacts the entire food chain associated with them. As a result of this phenomenon and other factors mentioned above, it is imperative to investigate how we can better protect our oceans’ biodiversity before it’s too late.
Key Takeaways
- Human activities have caused significant damage to marine biodiversity, with factors like climate change, pollution, overfishing, habitat destruction, and invasive species contributing to declining biodiversity.
- Seagrass beds provide vital habitat and food for many marine organisms, but are threatened by coastal development and boat traffic. Conservation efforts involve reducing nutrient pollution, regulating boat traffic, and implementing zoning laws.
- Invasive species pose a significant threat to native species and reduce diversity and productivity. Control measures like early detection and management strategies are necessary to minimize negative impacts.
- Coastal development leads to habitat destruction and changes in marine biodiversity, but eco-friendly resorts and beach nourishment programs can mitigate negative impacts. Preventing the introduction and spread of invasive species is crucial for maintaining healthy marine ecosystems.

Climate Change
Oh, no big deal, just the fact that our planet is slowly turning into a fiery hellscape thanks to climate change… but sure, let’s keep ignoring the impact it’s having on marine biodiversity.
The impact of climate change on marine ecosystems is a growing concern among scientists and conservationists alike. Rising temperatures are causing ocean currents to shift, which can affect the distribution and abundance of many marine species.
In addition to changes in ocean currents, climate change is also leading to increased acidity levels in seawater. As carbon dioxide (CO2) levels rise due to human activities like burning fossil fuels, more and more CO2 dissolves in the ocean water.
This creates carbonic acid and lowers the pH of seawater, making it more acidic. This process, known as ocean acidification, has already been shown to have negative effects on some marine organisms such as shellfish and corals.
As these organisms struggle to adapt or migrate away from areas with high acidity levels, entire ecosystems may be impacted.
Pollution
As you delve into the subtopic of pollution, it’s important to understand its various effects on marine biodiversity.
One major concern is the impact of plastic on marine life, as it can lead to entanglement and ingestion that ultimately disrupts food chains.
Additionally, chemical pollution from sources such as pesticides and industrial waste can accumulate in marine organisms, leading to negative health impacts for both wildlife and humans who consume them.
Finally, oil spills can have catastrophic impacts on entire ecosystems, causing widespread damage to habitats and populations alike.
Effects of Plastic on Marine Life
You’ll be shocked to learn how much harm plastic can cause to marine life. Plastic debris in the ocean is a major threat to marine biodiversity, as it has detrimental effects on various species of fish, mammals, and birds.
The impact on the food chain is significant as well, leading to changes in ecosystem dynamics. Plastic is not biodegradable and remains in the environment for hundreds of years. As it breaks down into smaller pieces called microplastics, it becomes more difficult to remove from the ocean and accumulates in fish tissues through ingestion or absorption.
This accumulation of plastic particles can lead to malnutrition, reduced reproductive success, and even death among marine organisms. It also poses a potential risk for human health when these contaminated fish are consumed by humans as seafood.
Therefore, reducing the use of single-use plastics and properly disposing of plastic waste are crucial steps towards protecting marine biodiversity.
Chemical Pollution
Chemical pollution poses a serious threat to the health of marine organisms and the overall well-being of ocean ecosystems. The discharge of chemicals from industrial plants, agricultural activities, and households can lead to negative impacts on marine biodiversity. These pollutants can accumulate in the tissues of marine animals, causing reproductive problems, mutations, and even death.
Furthermore, chemical pollution affects ecosystem health by altering nutrient cycles and disrupting food webs. Some chemicals can stimulate harmful algal blooms that deplete oxygen levels in seawater. This phenomenon is known as eutrophication and leads to large-scale fish kills. Other chemicals like heavy metals can interfere with enzyme activity in marine organisms leading to biochemical imbalances.
In conclusion, chemical pollution is a significant contributor to declining marine biodiversity worldwide. To protect our oceans’ health and restore their ecological balance, we must take action towards sustainable practices that reduce toxic waste discharges into coastal waters.
Oil Spills
If you’re not careful, an oil spill can really throw a wrench in the works of ocean ecosystems, potentially causing irreparable damage and putting marine life in hot water. Oil spills can have a devastating impact on marine biodiversity and lead to long-term environmental consequences.
Here are some of the ways that oil spills can affect ocean ecosystems:
- Oil spills release toxic chemicals into the water that can harm or kill fish, birds, and other aquatic creatures.
- Oil slicks create a physical barrier between the air and water, reducing the amount of oxygen that reaches underwater habitats.
- The cleanup process for oil spills often involves using chemical dispersants that can further harm marine life.
- The economic consequences of an oil spill can be severe for communities that rely on fishing or tourism industries.
- Oil spills can cause significant damage to shorelines and wetlands, disrupting fragile coastal ecosystems.
The impact of an oil spill on tourism cannot be overstated. Coastal communities that depend on tourism may see a significant drop in visitors following an oil spill due to concerns about safety and environmental impacts. Additionally, businesses such as hotels and restaurants may suffer losses if tourists avoid the area altogether.
Economic consequences are also felt by those who work in fishing industries since many species may become contaminated with harmful chemicals found in crude oil. It’s important to remember that preventing oil spills is key to preserving marine biodiversity and protecting our planet’s natural resources.
Overfishing
Overfishing has significantly contributed to the decline of marine biodiversity. Unsustainable fishing practices, such as bottom trawling, can destroy entire ecosystems and result in the depletion of fish populations. When certain species are overfished, it can have a domino effect on other species within that ecosystem.
For example, if a predator fish is overfished, its prey will likely increase in population and consume more of their own prey, causing an imbalance in the food chain. The economic impact of overfishing cannot be ignored either. Many coastal communities rely on commercial fishing for their livelihoods.
If fish populations continue to decline due to unsustainable practices, these communities will suffer financially. It’s important for governments and industry leaders to work together to implement sustainable fishing practices that protect both marine biodiversity and the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
Habitat Destruction
You need to understand that habitat destruction is a serious threat to marine biodiversity.
Coral reefs are being destroyed due to pollution, climate change, and overfishing.
Seagrass beds are also being damaged by human activities such as coastal development, dredging, and boat anchoring.
These factors have significant impacts on the health of our oceans and the species that inhabit them.

Destruction of Coral Reefs
When you visit a coral reef, it’s important to remember that your actions can have a significant impact on the health and survival of these delicate ecosystems.
Coral reefs are one of the most diverse and productive ecosystems in the world, providing habitat for an estimated 25% of all marine species.
Unfortunately, coral reefs are under threat from a multitude of factors, including destruction caused by human activity.
One major factor contributing to the destruction of coral reefs is coral bleaching. This occurs when corals expel their colorful algae due to stress caused by changes in temperature or other environmental factors, resulting in white or pale-colored corals that are more vulnerable to disease and death.
Another factor is ocean acidification, which occurs when carbon dioxide from human activities dissolves into seawater, making it more acidic. This makes it harder for corals to build their skeletons and leads to slower growth rates and reduced reproduction.
If we don’t take action now to reduce our impact on coral reefs through measures such as reducing carbon emissions and protecting important habitats from destructive practices like overfishing or pollution, we risk losing this vital ecosystem forever.
Destruction of Seagrass Beds
The destruction of seagrass beds, caused by factors such as coastal development and boat traffic, is leading to the loss of crucial habitats for a variety of marine species. Seagrasses play an important ecological role in providing shelter and food for many organisms, including commercially valuable fish species. The decline in seagrass populations can have ripple effects throughout the entire ecosystem.
Conservation efforts are being made to protect and restore seagrass beds. These efforts include reducing nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff and sewage discharge, regulating boat traffic in sensitive areas, and implementing zoning laws to limit coastal development.
By recognizing the ecological importance of seagrasses and taking action to protect them, we can help preserve biodiversity in our oceans.
Coastal Development
Coastal development has led to significant changes in marine biodiversity. The construction of hotels, resorts, and other infrastructure along the coastlines has resulted in the destruction of vital habitats such as seagrass beds. These habitats are crucial for a variety of marine species, including turtles, fish, and crustaceans.
Sustainable tourism practices can help mitigate the negative impact of coastal development on marine biodiversity. For instance, eco-friendly resorts that prioritize conservation efforts can reduce their carbon footprint and promote responsible practices among visitors. Additionally, measures such as beach nourishment programs can help combat coastal erosion caused by development.
It is essential to consider these factors when developing coastal regions to ensure that we do not further harm our oceans’ fragile ecosystems.
Invasive Species
Invasive species drastically reduce marine biodiversity by outcompeting native species for resources. The introduction of non-native species in an ecosystem can have severe impacts that ripple throughout the food web, leading to a decline in overall diversity and productivity.
Invasive species are often introduced through human activities such as shipping, aquaculture, and aquarium trade. Control measures must be put in place to prevent the spread of invasive species once they have established themselves in an ecosystem. Measures such as early detection, rapid response, and management strategies can help minimize the negative impacts of invasive species on marine biodiversity.
To better understand the impact of invasive species on marine ecosystems, impact assessments should be conducted before introducing any new non-native organisms. These assessments would evaluate the potential risks and consequences of introducing a new organism into an ecosystem. It is crucial to recognize the importance of preventing the introduction and spread of invasive species to maintain healthy marine ecosystems for future generations.
- Invasive species can lead to declines in native populations
- Introduced organisms may not have natural predators or competitors
- Human activities are primary causes for introducing invasive organisms
- Assessing potential impacts and implementing control measures are critical for managing invasions
Frequently Asked Questions
How does marine biodiversity impact human health?
You won’t believe how much marine biodiversity impacts your health! The diverse ecosystems provide essential services like food, clean water, and oxygen. Without them, human well-being would be in grave danger. Protecting marine biodiversity is crucial for our survival.
What role do ocean currents play in maintaining marine biodiversity?
Ocean currents play a crucial role in maintaining marine biodiversity by distributing nutrients and regulating temperature and salinity. However, pollution can disrupt these currents, leading to negative impacts on both the currents and the biodiversity they support.
How do marine protected areas contribute to the preservation of marine biodiversity?
Marine protected areas act as conservation strategies that contribute significantly to the preservation of marine biodiversity. These designated zones help protect and restore critical habitats and species, ensuring long-term sustainability of our oceans.
What are the economic impacts of declining marine biodiversity?
Picture a bustling city without its main source of income. The same goes for the fishing and tourism industries when marine biodiversity declines. Fewer species mean fewer catches and fewer attractions, resulting in economic losses.
How do cultural beliefs and practices affect marine biodiversity conservation efforts?
To effectively conserve marine biodiversity, conservation strategies must incorporate Indigenous knowledge and cultural practices. This includes considering traditional fishing methods and community-based management systems, as they have been shown to promote sustainable resource use.
Sponsor: Rapid Fix Garage Doors in Caboolture QLD