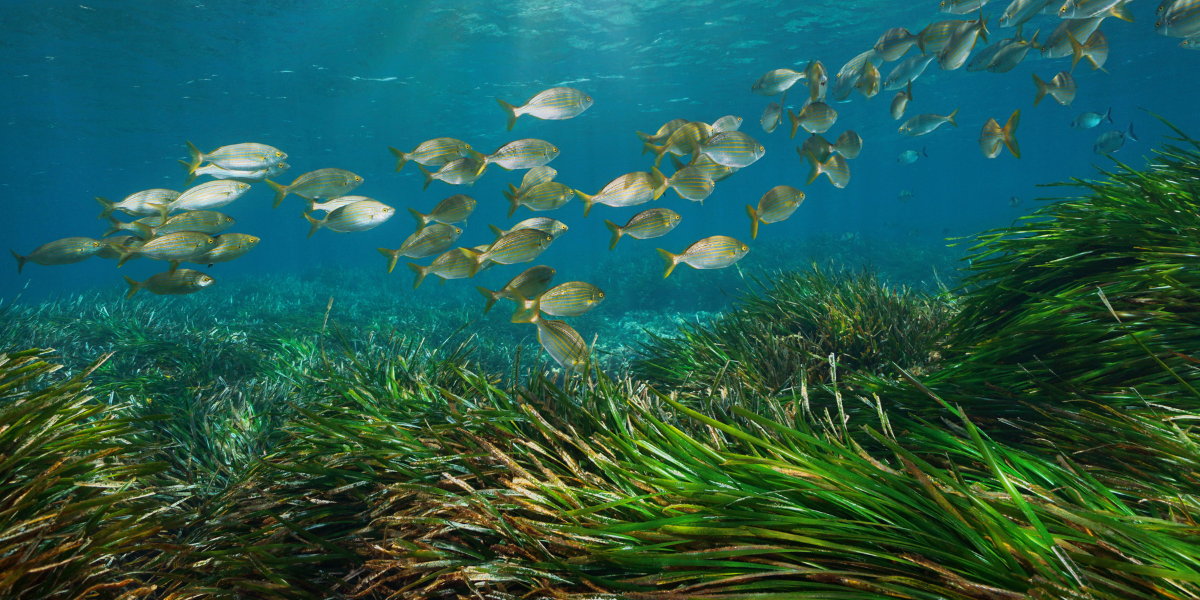
You may have heard that the ocean is the lungs of our planet, but did you know that seagrass beds are one of the most valuable resources in this ecosystem? In fact, they are often referred to as ‘the rainforest of the sea’due to their incredible biodiversity and importance in supporting marine life.
These underwater meadows play a vital role in maintaining healthy oceans, from acting as a nursery ground for young fish and other creatures to improving water quality and even combating climate change.
Seagrass beds cover less than 0.2% of the world’s oceans, yet they support an astonishing 20% of all marine species. They provide habitat for countless organisms such as crabs, shrimp, sea turtles, and dugongs (or manatees), which graze on the seagrass leaves.
As a nursery ground for juvenile fish, these beds help maintain stable populations of commercially important species like snapper and grouper. In addition to providing shelter and food, seagrasses also offer protection from predators by reducing water flow and turbulence near the ocean floor.
The role that these underwater meadows play in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems cannot be overstated – they are truly a cornerstone of ocean life.
Key Takeaways
- Seagrass beds cover less than 0.2% of the world’s oceans but support 20% of all marine species, providing habitat for various organisms and acting as a nursery ground for juvenile fish.
- They are under threat from human activities such as coastal development, pollution, and overfishing, but conservation efforts focus on promoting sustainable fishing practices and reducing nutrient runoff into coastal waters, as well as restoration to bring back degraded ecosystems and promote biodiversity.
- Seagrass beds play a significant role as a food source for many species, support commercial fisheries worth billions of dollars annually, and attract tourists.
- They also have important environmental benefits, such as absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, acting as water quality indicators by filtering pollutants and sediment from coastal waters, and maintaining healthy levels of dissolved oxygen, which is vital for many aquatic organisms’ survival.
Importance of Seagrass Beds in Marine Ecosystems
You might not realize it, but seagrass beds are like the bustling cities of the ocean, providing crucial habitat and food for countless species. These underwater meadows are home to a wide variety of marine life, including fish, crabs, shrimp, sea turtles, and dugongs.
Seagrass also plays an important role in stabilizing sediments and protecting coastlines from erosion. Despite their importance, seagrass beds are under threat from a range of human activities including coastal development, pollution, and overfishing.
As a result, many seagrass ecosystems have been lost or degraded over time. To address this issue and protect these valuable habitats for future generations, seagrass conservation efforts have focused on promoting sustainable fishing practices and reducing nutrient runoff into coastal waters.
In addition to conservation efforts, there’s also growing interest in seagrass restoration as a way to bring back degraded ecosystems and promote biodiversity in our oceans.
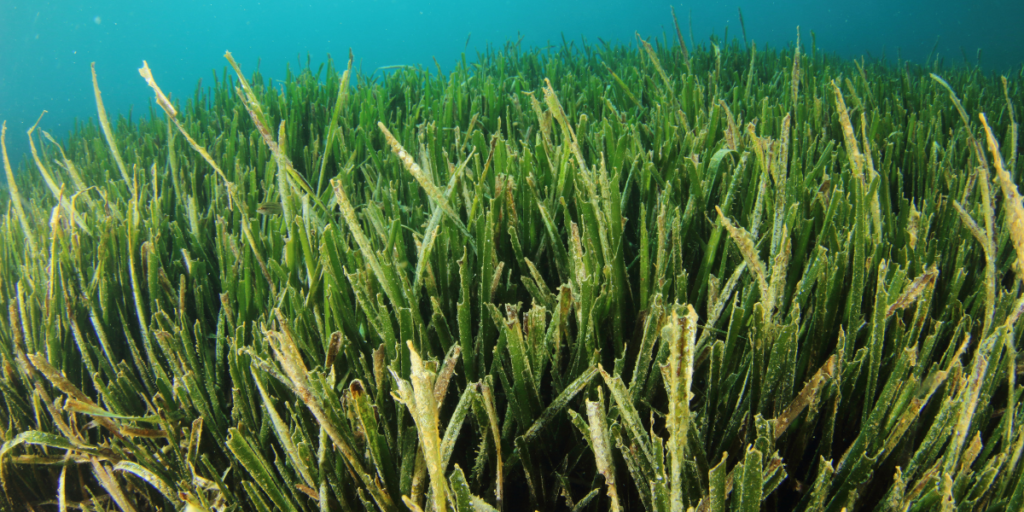

Seagrass Beds as a Nursery Ground
Seagrass meadows serve as a crucial breeding ground for a variety of fish and other aquatic creatures. These underwater meadows provide an ideal nursery habitat for many species of juvenile fish, such as snapper, grouper, and sea bream. Seagrasses offer excellent shelter from predators and strong currents while providing ample food sources in the form of algae, small crustaceans, and other invertebrates.
The ecological significance of seagrass beds is immense. They not only serve as nurseries but also help mitigate climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere at a rate up to 35 times faster than tropical rainforests. Additionally, seagrasses act as water quality indicators by filtering pollutants and sediment from coastal waters before they reach deeper offshore habitats.
Their economic benefits are also significant; they support commercial fisheries worth billions of dollars annually and attract tourists who come to enjoy the beautiful scenery and recreational activities offered by these unique ecosystems.
Seagrass Beds as a Food Source
Feasting on the abundance of small crustaceans and invertebrates found in seagrass meadows can be a delicious and nutritious meal for many marine animals.
Seagrass beds play a significant role as a food source for many species, including fish, sea turtles, manatees, and sea urchins. These animals rely on seagrass meadows to provide them with essential nutrients that help them grow, reproduce, and survive.
Seagrass beds are vital for trophic interactions within marine ecosystems. They support various levels of the food chain by providing primary producers such as algae and seagrasses that are consumed by herbivorous animals like sea turtles and dugongs. Predators then feed on these herbivores, maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
Additionally, some organisms use seagrass beds as hunting grounds to ambush their prey or seek refuge from predators. Overall, seagrass beds provide an important foundation for marine food webs that ultimately sustain many valuable commercial fisheries.
Seagrass Beds and Water Quality
As you dive into the topic of seagrass beds and water quality, you’ll discover that these underwater meadows play a critical role in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems.
One way they do this is by absorbing nutrients from the water column, which can prevent harmful algal blooms and other negative consequences of nutrient pollution.
Additionally, seagrass beds are effective at trapping sediment, thereby reducing turbidity and improving water clarity for photosynthetic organisms like seagrasses themselves.
Absorption of Nutrients
By absorbing nutrients from the water column, seagrass beds provide an important service to marine ecosystems. Nutrient cycling is a crucial process that maintains ecological balance in the oceans, and seagrass beds play a significant role in this process. They absorb nitrogen and phosphorus from the water column, which are essential elements for plant growth.
As they take up these nutrients, they reduce their concentration in the water column, preventing excessive nutrient loading that can lead to harmful algal blooms and other negative impacts on marine life. The absorption of nutrients by seagrass beds not only benefits the plants themselves but also supports other organisms within the ecosystem.
Seagrass meadows provide habitats for a wide range of species such as fish, crustaceans, and mollusks, which rely on these environments for food and shelter. By taking up excess nutrients from the water column, seagrasses help maintain healthy levels of dissolved oxygen, which is vital for many aquatic organisms’ survival.
In this way, the nutrient-absorbing capabilities of seagrass beds contribute significantly to maintaining a healthy marine ecosystem.
Trapping of Sediment
Trapping sediment is a critical function of seagrass meadows, helping to prevent erosion and protect the delicate balance of coastal ecosystems. Seagrass leaves create a complex matrix that slows down water flow and allows sediments to settle. This process not only helps stabilize the seafloor but also provides a substrate for other organisms to attach and grow on.
The sediment entrapment by seagrass beds has several benefits for marine ecosystems. Here are some examples:
- Sediment trapping reduces the amount of suspended particles in the water column, improving water clarity and facilitating photosynthesis in underwater plants.
- The deposition of organic matter associated with sedimentation contributes to nutrient cycling and supports the food web.
- Seagrasses can accumulate heavy metals and pollutants from surrounding waters through sediment entrapment, reducing their impact on other organisms.
- The ability of seagrasses to trap sediments helps maintain shoreline stability by buffering wave energy and preventing erosion.
- Finally, sediment entrapment may provide a mechanism for carbon storage in coastal ecosystems, as organic matter accumulates over time.

Improvement of Water Clarity
The crystal-clear waters of a thriving seagrass meadow provide a window into the mesmerizing underwater world, where sunlight illuminates colorful corals and schools of fish dart among waving fronds.
Seagrass beds play a crucial role in improving water clarity by trapping suspended sediment particles that would otherwise cloud the water column. By doing so, they create an environment that is perfect for photosynthesis, allowing light to penetrate deeper into the water and supporting the growth of marine plants such as algae.
Apart from providing us with stunning views of marine life, seagrass beds also offer numerous benefits to fisheries and local economies. Improved water clarity can increase primary productivity, which in turn supports more fish biomass. This enhanced productivity provides food resources for commercial and recreational fishing activities and helps maintain healthy populations of economically valuable species like oysters and clams.
Therefore, preserving seagrass meadows is not only important for their intrinsic ecological value but also for their significant economic impact on coastal communities.
Seagrass Beds and Carbon Sequestration
Seagrass beds, just like forests on land, play a vital role in mitigating climate change by absorbing and storing large quantities of carbon dioxide. These underwater meadows can sequester up to 83,000 metric tons of carbon per square kilometer, which is more than twice the average amount stored in terrestrial ecosystems.
Here are three reasons why seagrass beds are excellent carbon sinks:
- Seagrasses have high rates of photosynthesis: Seagrasses are some of the fastest-growing plants on Earth and can capture large amounts of atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis. They convert this carbon into organic matter and release oxygen back into the water.
- Seagrass beds trap sediment: The roots and leaves of seagrasses trap sediment particles that would otherwise be suspended in the water column, reducing light penetration and inhibiting photosynthesis. This allows for greater accumulation of organic matter on the seafloor.
- Seagrass meadows have long lifespans: Unlike other marine plants that only survive for a few years, seagrasses can live for decades or even centuries. As they grow taller and wider over time, their capacity to store carbon increases as well.
Maintaining healthy seagrass ecosystems is crucial for mitigating climate change by acting as important carbon sinks that absorb significant amounts of atmospheric CO2 from our atmosphere every year.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all seagrass species equally important in marine ecosystems?
You may be surprised to learn that not all seagrass species are equally important in marine ecosystems. Ecological importance and genetic diversity vary among species, with some providing more benefits than others.
Can seagrass beds be artificially created and maintained in marine environments?
You can create artificial seagrass beds using techniques such as planting or transplanting. Maintenance involves monitoring water quality, removing debris and invasive species. Like a garden, it requires nurturing to thrive and provide benefits to the surrounding marine ecosystem.
How does climate change affect seagrass beds and their role in marine ecosystems?
Climate change affects seagrass beds by causing ocean acidification and sea level rise, which reduces the amount of light available for photosynthesis and disturbs sediment stability. These changes can lead to declines in seagrass abundance and negatively impact their role in marine ecosystems.
What is the impact of human activities such as fishing or boating on seagrass beds?
Overfishing impacts seagrass beds by reducing the population of herbivorous species that help maintain the ecosystem. Boat traffic disturbance can cause physical damage to the plants and increase sedimentation, which can also harm seagrass beds. These activities must be mitigated to preserve this important marine habitat.
Are there any negative effects of seagrass beds on marine ecosystems or other species?
Seagrass beds can have negative ecological impacts on other species, such as creating areas of low oxygen and altering sediment composition. However, restoration efforts have shown promise in mitigating these effects and promoting healthy marine ecosystems.
Our sponsors: Rapid Fix Garage Doors are your one-stop shop for all garage door repair serices in moreton bay region QLD.