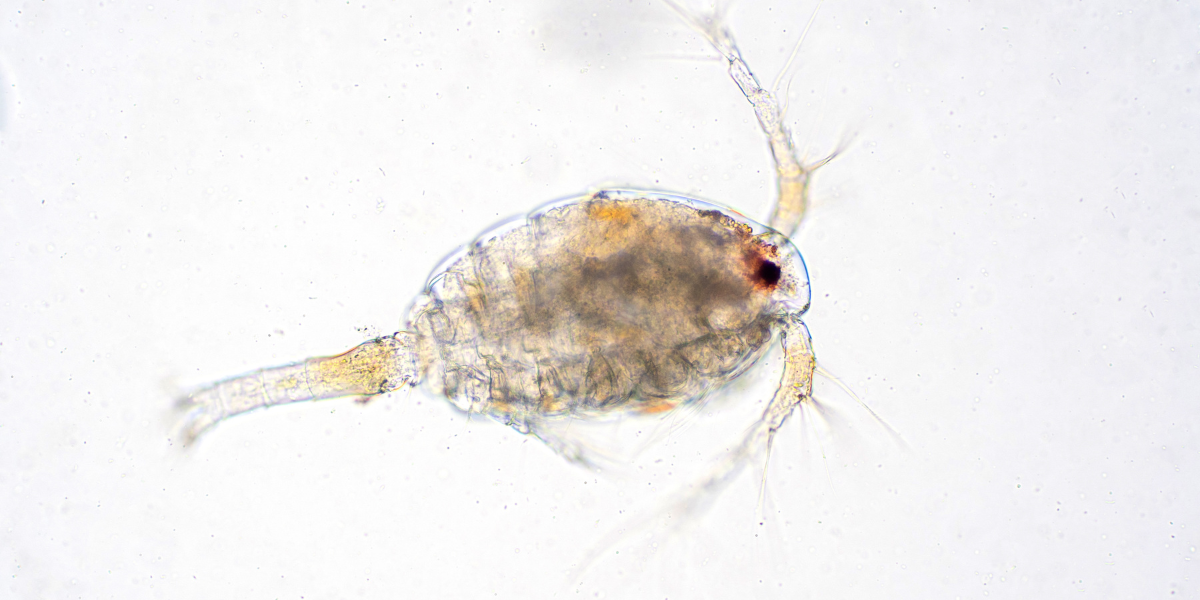
If you have ever taken a dip in the ocean, chances are that you have encountered plankton. These tiny organisms form the foundation of marine food webs and play a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. Despite their importance, many people are unaware of the vital role that plankton plays in our oceans and how their conservation is linked to our own survival.
Plankton refers to any organism that drifts or floats passively with the ocean currents rather than swimming against them. They can be classified into two main groups: phytoplankton (plant-like) and zooplankton (animal-like).
Phytoplankton are responsible for producing half of the oxygen on Earth through photosynthesis, while zooplankton serve as a critical food source for larger marine animals such as fish, whales, and sea birds. The complex interactions between these tiny creatures form the basis of marine ecosystems and impact everything from climate change to fisheries production.
Key Takeaways
- Plankton serve as the primary food source for many marine species and up to 90% of all marine life depends on them for survival.
- Phytoplankton produce half of Earth’s oxygen through photosynthesis and convert carbon dioxide into organic matter, while zooplankton serve as a critical food source for larger marine animals and excrete nutrients back into the water column.
- Plankton play an important role in nutrient cycling and regulating Earth’s climate, sequestering significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Plankton populations are declining due to overfishing and pollution, and conservation efforts such as reducing carbon footprint, supporting sustainable fishing practices, and creating marine protected areas are crucial for their survival and the health of marine ecosystems.
The Definition and Classification of Plankton
Plankton, which can be classified as either phytoplankton or zooplankton, are the tiny organisms that drift in our oceans. They are unable to swim against currents and instead rely on water movements to transport them.
Phytoplankton are plant-like and photosynthesize using energy from the sun, while zooplankton are animal-like and consume other plankton for food.
Classification of plankton is based on their size range. The term ‘plankton’ refers to organisms that range in size from less than one micron (such as bacteria) up to several centimeters (such as jellyfish). Within this size range there are additional subcategories: picoplankton (less than 0.2 microns), nanoplankton (0.2-20 microns), microplankton (20-200 microns), mesoplankton (200-2000 microns) and macroplankton (>2 mm).
Understanding these classifications is important when studying marine ecosystems because different types of plankton play unique roles within the food web.
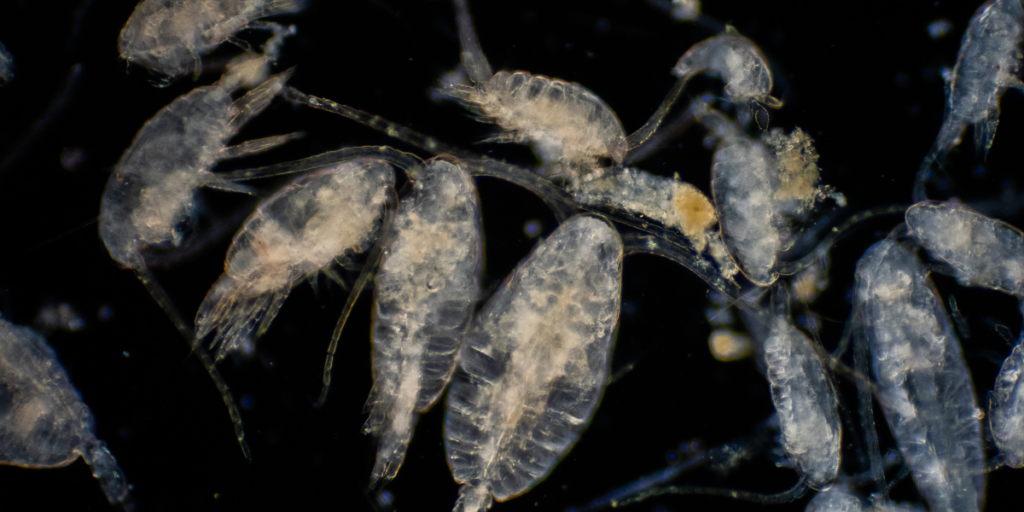

The Role of Plankton in the Marine Food Web
You rely on a complex network of tiny organisms to sustain the vast oceanic food web. Plankton, being among the most important members of this network, plays a crucial role in maintaining marine ecosystems.
Plankton serve as the primary food source for many marine species, including small fish, zooplankton, and filter feeders such as whales and baleen sharks. In fact, it’s estimated that up to 90% of all marine life depends directly or indirectly on plankton for their survival.
In addition to serving as a food source, plankton also play an important role in nutrient cycling in marine ecosystems. Phytoplankton use energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide into organic matter through photosynthesis. This organic matter is then consumed by other organisms, which release nutrients back into the water when they excrete waste or die.
These nutrients are then used by phytoplankton to continue the cycle of growth and consumption. Without this vital role played by plankton, nutrient levels in oceans would become depleted over time, resulting in a collapse of entire marine ecosystems.
Plankton and Carbon Sequestration
Did you know that these tiny organisms can help mitigate climate change by sequestering significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
Plankton, both phytoplankton (plant-like) and zooplankton (animal-like), play a crucial role in carbon sequestration. They absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, converting it into organic matter that sinks to the bottom of the ocean. This process is known as the biological pump.
Plankton also play a role in nutrient cycling and ocean acidification. Phytoplankton require nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus for growth. Zooplankton feed on phytoplankton and excrete nutrients back into the water column, making them available for other organisms to use.
However, with increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere leading to ocean acidification, plankton populations may be negatively affected which could have cascading effects throughout marine ecosystems.
Overall, understanding the complex interactions between plankton and their environment is critical for predicting how marine ecosystems will respond to ongoing climate change.
Plankton and Climate Change
As you delve into the topic of Plankton and Climate Change, one key point to consider is the impact of climate change on plankton populations.
With rising sea temperatures and changes in ocean chemistry, many species of plankton are struggling to adapt. This decline can have far-reaching implications for marine ecosystems, as plankton form the base of the food chain and play a crucial role in carbon sequestration.
It’s important to understand these complex interactions as we strive to mitigate the effects of climate change on our oceans.

The Impact of Climate Change on Plankton
When climate change affects plankton populations, the entire marine ecosystem is impacted. Plankton migration patterns are changing due to rising sea temperatures and altered ocean currents. This can lead to a mismatch between the timing of plankton blooms and the arrival of fish larvae that rely on them for food, which can have cascading effects throughout the food web.
Additionally, ocean acidification caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is affecting the ability of some species of plankton to form their shells. This not only impacts their survival but also has implications for other organisms that rely on them as a food source.
Overall, understanding how climate change is impacting plankton populations is crucial in predicting future changes in marine ecosystems and developing effective conservation strategies.
The Implications of Plankton Decline
The decline of plankton populations has significant implications for the health and productivity of the world’s oceans, affecting everything from fisheries to carbon storage. Plankton plays a crucial role in marine ecosystems as they form the base of the food chain, providing sustenance for larger organisms such as whales, fish, and birds. However, due to overfishing and pollution, their numbers are rapidly declining.
Here are some implications of this decline:
- Reduced fish populations: As plankton serves as a primary food source for many species of fish, their decrease in numbers can lead to reduced fish populations.
- Decreased oxygen production: Plankton is responsible for producing around 50% of the oxygen we breathe. The reduction in their numbers could have severe consequences on our planet’s atmospheric composition.
- Altered carbon cycles: Plankton also plays a significant role in regulating the Earth’s climate by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. A reduction in plankton could lead to increased levels of atmospheric CO2.
- Increased algal blooms: When there is an excess amount of nutrients in the water due to pollution or agricultural runoff, it can cause harmful algal blooms that can be toxic to both humans and marine life.
- Impacts on biodiversity: The loss of plankton could lead to a cascading effect on other species within marine ecosystems, causing a decline in overall biodiversity.
It’s imperative that we take action now to mitigate these negative impacts before it’s too late. Reducing overfishing and addressing pollution are critical steps towards protecting these vital organisms and preserving our oceans’ health.
Conservation Efforts for Plankton and Marine Ecosystems
You can actively participate in conservation efforts for plankton and marine ecosystems by reducing your carbon footprint and supporting sustainable fishing practices. One way to reduce your carbon footprint is to decrease your use of single-use plastics, such as straws, bags, and water bottles. Plastics can break down into tiny microplastics that are ingested by plankton and other marine organisms, leading to harmful effects on their health.
Additionally, you can choose to use public transportation or carpool instead of driving alone to reduce emissions. Another way to support conservation efforts is by advocating for the establishment of more marine protected areas (MPAs) and supporting sustainable fishing practices.
MPAs are designated areas where human activity is restricted or prohibited in order to protect the biodiversity and ecosystem services provided by the area. These protected areas not only benefit the plankton populations but also provide habitats for larger marine animals such as fish, whales, and sea turtles.
Supporting sustainable fishing practices means choosing seafood that has been harvested using methods that minimize harm to non-target species like plankton. This includes avoiding overfished species and purchasing seafood from sources that follow responsible fishing guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are all species of plankton beneficial to marine ecosystems?
Did you know that harmful species of plankton can cause ecological impacts by producing toxins that harm marine life? While not all species are harmful, it’s important to monitor their populations and understand their impact on the ecosystem.
Can the overfishing of certain fish species affect the abundance of plankton in the ocean?
Overfishing can impact the abundance of plankton in the ocean by reducing the number of fish that eat them. This can lead to a plankton bloom, which may seem beneficial but can actually harm marine ecosystems by depleting oxygen and creating toxic conditions.
How does pollution and human activity affect the growth and survival of plankton?
As you dive into the topic of plankton, consider how pollution can stunt their growth and human activity can threaten their survival. Harmful substances and changes in temperature disrupt their delicate balance, ultimately impacting the entire marine food chain.
Are there any negative consequences to the increased presence of plankton in certain areas of the ocean?
If plankton blooms occur too frequently or in large amounts, they can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels. This can result in the creation of dead zones which harm marine life and ecosystems. Environmental factors such as pollution and climate change can contribute to this negative consequence.
How do scientists study and monitor the populations and behaviors of plankton in the ocean?
The ocean is a vast and complex ecosystem, but scientists use sampling methods to collect plankton specimens for analysis. They also utilize remote sensing technology to monitor their movements, much like astronomers studying the stars in the sky.
Our sponsors: Rapid Fix Garage Doors are your one stop shop for all garage door repair services in moreton bay region QLD.